ex4-NN back propagation
AndrewNg 机器学习习题ex4-NN back propagation
需要的头:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import scipy.io as sio
import matplotlib
import scipy.optimize as opt
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report # 这个包是评价报告
Visualizing the data
载入数据:
def load_data(path, transpose=True):
data = sio.loadmat(path)
y = data.get('y')
y = y.reshape(y.shape[0])
X = data.get('X')
if transpose:
X = np.array([im.reshape((20, 20)).T for im in X])
X = np.array([im.reshape(400) for im in X])
return X, y
X, y = load_data('./data/ex4data1.mat')
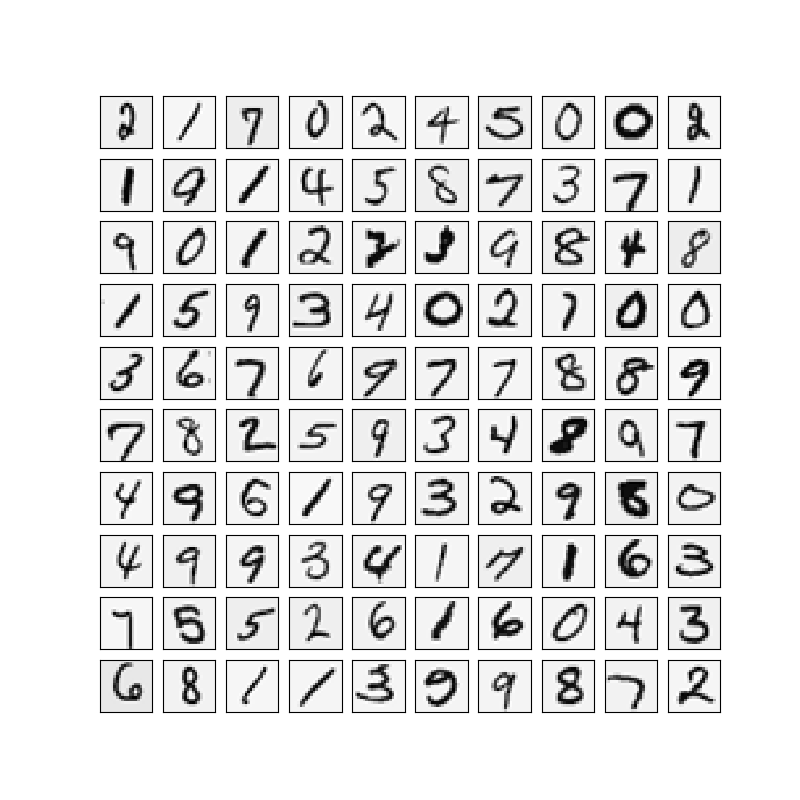
def plot_100_image(X):
size = int(np.sqrt(X.shape[1]))
sample_idx = np.random.choice(np.array(X.shape[0]), 100)
sample_images = X[sample_idx, :]
fig, ax_array = plt.subplots(nrows=10, ncols=10, sharey=True, sharex=True, figsize=(8, 8))
for r in range(10):
for c in range(10):
ax_array[r, c].matshow(sample_images[10 * r + c].reshape((size, size)), cmap=matplotlib.cm.binary)
plt.xticks(np.array([]))
plt.yticks(np.array([]))
plt.show()
plot_100_image(X)
准备数据
特征集合X添加一列全为1的偏差向量,把目标向量y进行OneHot编码。
X_raw, y_raw = load_data('./data/ex4data1.mat', transpose=False) # 这里转置
X = np.insert(X_raw, 0, np.ones(X_raw.shape[0]), axis=1) # 增加全为1的一列
print(y.shape) # (5000,)
y = np.array([y_raw]).T
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder
encoder = OneHotEncoder(sparse=False)
y_onehot = encoder.fit_transform(y)
print(y_onehot.shape) # (5000, 10)
读取权重
先读取出ex4weights.mat中的theta1和theta2,把theta展开后进行扁平化处理。
def load_weight(path):
data = sio.loadmat(path)
return data['Theta1'], data['Theta2']
t1, t2 = load_weight('./data/ex4weights.mat')
print(t1.shape, t2.shape) # (25, 401) (10, 26)
def serialize(a, b):
# np.ravel() 降维
# np.concatenate() 拼接
return np.concatenate((np.ravel(a), np.ravel(b)))
def deserialize(seq):
# 解开为两个theta
return seq[:25 * 401].reshape(25, 401), seq[25 * 401:].reshape(10, 26)
theta = serialize(t1, t2)
print(theta.shape) # (25 * 401) + (10 * 26) = 10285
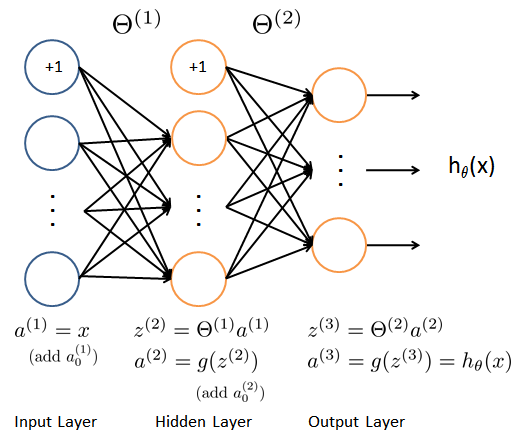
前向传播 feed forward
(400 + 1) -> (25 + 1) -> (1)
def sigmoid(z):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-z))
def feed_forward(theta, X):
t1, t2 = deserialize(theta)
m = X.shape[0]
a1 = X # 5000 * 401
z2 = a1 @ t1.T
a2 = np.insert(sigmoid(z2), 0, np.ones(m), axis=1) # 5000*26 第一列加一列一
z3 = a2 @ t2.T # 5000 * 100
h = sigmoid(z3) # 5000 * 10 这是 h_theta(X)
return a1, z2, a2, z3, h # 把每一层的计算都返回
#_, _, _, _, h = feed_forward(theta, X)
#print(h.shape) # (5000, 10)
代价函数与正则化


def cost(theta, X, y):
m = X.shape[0]
_, _, _, _, h = feed_forward(theta, X)
pair_computation = -np.multiply(y, np.log(h)) - np.multiply((1 - y), np.log(1 - h))
return pair_computation.sum() / m
cost_res = cost(theta, X, y)
print("cost:",cost_res)
def regularized_cost(theta, X, y, l=1):
t1, t2 = deserialize(theta) # t1: (25,401) t2: (10,26)
m = X.shape[0]
reg_t1 = np.power(t1[:, 1:], 2).sum()
reg_t2 = np.power(t2[:, 1:], 2).sum()
reg = (1 / (2 * m)) * (reg_t1 + reg_t2)
return cost(theta, X, y) + reg
regularized_cost_res = regularized_cost(theta, X, y)
print("reg cost:",regularized_cost_res)
反向传播
def sigmoid_gradient(z):
return np.multiply(sigmoid(z), 1 - sigmoid(z))
print(sigmoid_gradient(0)) #0.25
def gradient(theta, X, y):
t1, t2 = deserialize(theta)
m = X.shape[0]
deltal = np.zeros(t1.shape)
delta2 = np.zeros(t2.shape)
a1, z2, a2, z3, h = feed_forward(theta, X)
for i in range(m):
a1i = a1[i, :]
z2i = z2[i, :]
a2i = a2[i, :]
hi = h[i, :]
yi = y[i, :]
d3i = hi - yi
z2i = np.insert(z2i, 0, np.ones(1))
d2i = np.multiply(t2.T @ d3i, sigmoid_gradient(z2i))
delta2 += np.matrix(d3i).T @ np.matrix(a2i)
deltal += np.matrix(d2i[1:]).T @ np.matrix(a1i)
delta1 = deltal / m
delta2 = delta2 / m
return serialize(delta1, delta2)
d1, d2 = deserialize(gradient(theta, X, y))
print(d1.shape, d2.shape) # (25, 401) (10, 26)
梯度校验
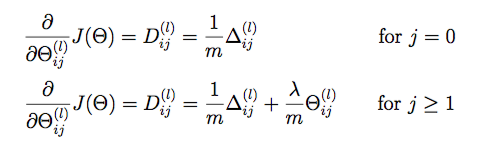
梯度正则化:
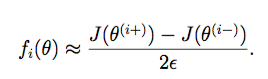
def regularized_gradient(theta, X, y, l=1):
"""don't regularize theta of bias terms"""
m = X.shape[0]
delta1, delta2 = deserialize(gradient(theta, X, y))
t1, t2 = deserialize(theta)
t1[:, 0] = 0
reg_term_d1 = (l / m) * t1
delta1 = delta1 + reg_term_d1
t2[:, 0] = 0
reg_term_d2 = (l / m) * t2
delta2 = delta2 + reg_term_d2
return serialize(delta1, delta2)
def expand_array(arr):
"""replicate array into matrix
[1, 2, 3]
[[1, 2, 3],
[1, 2, 3],
[1, 2, 3]]
"""
# turn matrix back to ndarray
return np.array(np.matrix(np.ones(arr.shape[0])).T @ np.matrix(arr))
def gradient_checking(theta, X, y, epsilon, regularized=False):
def a_numeric_grad(plus, minus, regularized=False):
"""calculate a partial gradient with respect to 1 theta"""
if regularized:
return (regularized_cost(plus, X, y) - regularized_cost(minus, X, y)) / (epsilon * 2)
else:
return (cost(plus, X, y) - cost(minus, X, y)) / (epsilon * 2)
theta_matrix = expand_array(theta) # expand to (10285, 10285)
epsilon_matrix = np.identity(len(theta)) * epsilon
plus_matrix = theta_matrix + epsilon_matrix
minus_matrix = theta_matrix - epsilon_matrix
# calculate numerical gradient with respect to all theta
numeric_grad = np.array([a_numeric_grad(plus_matrix[i], minus_matrix[i], regularized)
for i in range(len(theta))])
# analytical grad will depend on if you want it to be regularized or not
analytic_grad = regularized_gradient(theta, X, y) if regularized else gradient(theta, X, y)
# If you have a correct implementation, and assuming you used EPSILON = 0.0001
# the diff below should be less than 1e-9
# this is how original matlab code do gradient checking
diff = np.linalg.norm(numeric_grad - analytic_grad) / np.linalg.norm(numeric_grad + analytic_grad)
print('If your backpropagation implementation is correct,\nthe relative difference will be smaller than 10e-9 (assume epsilon=0.0001).\nRelative Difference: {}\n'.format(diff))
# gradient_checking(theta, X, y, epsilon= 0.0001)#这个运行很慢,谨慎运行
If your backpropagation implementation is correct,
the relative difference will be smaller than 10e-9 (assume epsilon=0.0001).
Relative Difference: 2.1466000818218673e-09
准备训练模型
def random_init(size):
return np.random.uniform(-0.12, 0.12, size)
def nn_training(X, y):
init_theta = random_init(10285) # 25 * 401 + 10 * 26
res = opt.minimize(fun=regularized_cost,
x0=init_theta,
args=(X ,y, 1),
method='TNC',
jac=regularized_gradient,
options={'maxiter': 400})
return res
res = nn_training(X, y) # 慢
print(res)
Out put:
fun: 0.32211992072588747
jac: array([ 2.15004329e-04, 3.88985627e-08, -3.33174201e-08, ...,
3.15328424e-05, 2.82831419e-05, -1.68082404e-05])
message: 'Max. number of function evaluations reached'
nfev: 400
nit: 26
status: 3
success: False
x: array([ 0.00000000e+00, 1.94492814e-04, -1.66587101e-04, ...,
-7.15493763e-01, -1.36561388e+00, -2.90127262e+00])
显示准确率
_, y_answer = load_data('./data/ex4data1.mat')
final_theta = res.x
def show_accuracy(theta, X, y):
_, _, _, _, h = feed_forward(theta, X)
y_pred = np.argmax(h, axis=1) + 1
print(classification_report(y, y_pred))
show_accuracy(final_theta, X, y_answer)
Out Put:
precision recall f1-score support
1 1.00 0.79 0.88 500
2 0.73 1.00 0.85 500
3 0.82 0.99 0.89 500
4 1.00 0.89 0.94 500
5 1.00 0.86 0.92 500
6 0.94 0.99 0.97 500
7 0.99 0.81 0.89 500
8 0.94 0.95 0.95 500
9 0.96 0.95 0.95 500
10 0.96 0.98 0.97 500
avg / total 0.93 0.92 0.92 5000
显示隐藏层
def plot_hidden_layer(theta):
"""
theta: (10285, )
"""
final_theta1, _ = deserialize(theta)
hidden_layer = final_theta1[:, 1:] # ger rid of bias term theta
fig, ax_array = plt.subplots(nrows=5, ncols=5, sharey=True, sharex=True, figsize=(5, 5))
for r in range(5):
for c in range(5):
ax_array[r, c].matshow(hidden_layer[5 * r + c].reshape((20, 20)),
cmap=matplotlib.cm.binary)
plt.xticks(np.array([]))
plt.yticks(np.array([]))
plot_hidden_layer(final_theta)
plt.show()
